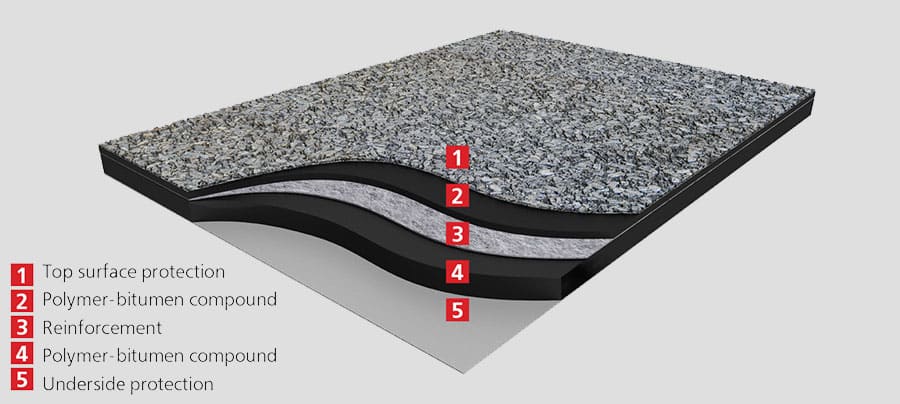

Components of Bituminous Membrane
The most widespread materials for the creation of the waterproofing layer are the polymer-bitumen roll-fed membranes. This is due to the relative simplicity of installation, the popularity of the technology, durability of the material and stability of the factory-set technical parameters. Polymer-bitumen membranes are commonly used for waterproofing of foundations, engineering structures, roads, bridge decks and flat roofs. These materials could also be used as an underlay for pitched roofs and as a vapour barrier.
The waterproofing membrane not only protects the internal premises from water penetrating inside, reducing their operating ability, disturbing the process equipment operation and worsening the microclimatic conditions indoors, but it also prevents the destruction of the foundation and supporting structures. Therefore, the correct selection and installation of the waterproofing membrane also ensure the durability of the whole facility.
Polymer-bitumen membranes undergo the effects of many unfavourable factors from the external environment. Changes in the surrounding temperature can cause deformations of the material and the base on which it is installed. The ability to withstand such deformations is the most important characteristic of roofing and waterproofing material and it depends on many components used in the production stage.
Polymer-bitumen Compound
The compound is a specially formulated mixture of bitumen and polymers. The main difference between compound types is the kind of polymer used:

APP
APP polymer provides additional flow resistance that makes it
possible to use the material in a very hot climate.
The limitation is that the material is less elastic and flexible at low
temperatures.

SBS
SBS polymer provides additional flexibility and dynamic
resistance.
It cannot be used in a very hot climate as a cap sheet membrane, because the
polymer does not grant high flow resistance to the material.
Special anti-root additives can be added to the polymer-bitumen compound to make it resistant to root penetration and ensure the reliable waterproofing of green roofs and foundations.
Reinforcement
- Glass fiber provides additional dimensional stability but does not grant elongation properties. Fiber glass felts have more resistance to moisture due to the porosity of the sheets. Silica sand is the prominent component of fiber glass felts and is combined with a number of selected elements and oxides.
- Polyester Provides excellent elongation properties and grants optimal strength to the material. Polyester provides superior thermal shock resistance, excellent fatigue endurance, puncture resistance and crack bridging capabilities. Polyester also exhibits high puncture resistance; tear strength and the durability to withstand high roof traffic.
Polymer Film
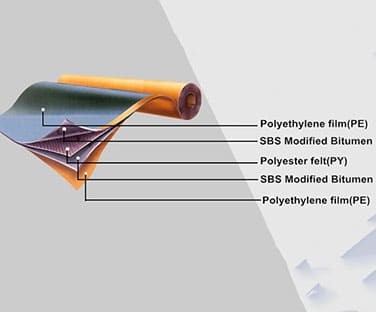
- Thin polymer film is used for underside surface protection from sticking in the roll. The film is covered with special graphics indicators for easier and more reliable torch-on installation. The film is melting during heating. If graphics becomes completely fused (surface is all black), the material is overheated. The material is heated properly when graphics is deformed, but visible.
- Polymer film without graphic elements is used as top surface protection of underlay membranes and membranes designed for waterproofing of foundations and engineering structures.
- Perforated polymer film can be used as underside protection to ensure even points of adhesion distribution and increase the speed of installation of the material.





